Abstract
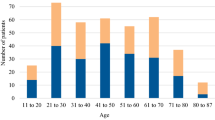
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is rarely analyzed in peripheral facial palsy, and reports in the literature are scarce. We report the CSF findings in 265 patients with acute isolated peripheral facial palsy. The CSF findings were abnormal in 11% of 230 patients with idiopathic peripheral facial palsy, in 60% of 17 patients with Ramsay Hunt syndrome (pleocytosis), in 25% of 8 patients with Lyme disease, in all of 8 patients with HIV infection, and in 2 other patients (sarcoidosis and herpes simplex). We conclude from this large series that the CSF is usually normal in idiopathic peripheral facial palsy. If the CSF is abnormal, a specific cause should be sought.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 17 October 1997 Accepted: 24 June 1998
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kohler, A., Chofflon, M., Sztajzel, R. et al. Cerebrospinal fluid in acute peripheral facial palsy. J Neurol 246, 165–169 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004150050328
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004150050328